Gum disease occurs when the surrounding tissue that provides support to your teeth becomes infected. This will cause the surrounding area to become inflamed, sensitive, red and prone to bleeding.
Bad breath and sponginess of the gums may also form, as the plaque deposits accumulate and continue to irritate the gums. Over time, the plaque will harden to form calculus or tartar. These deposits can only be removed by a dental health professional and if left untreated can lead to more underlying health problems.
There are 2 main types of gum disease – gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the initial stage of periodontal disease which causes gums to become inflamed, and vulnerable to bleeding. The affected area will be more sensitive, and the gums may also bleed easily when brushed. It is important to seek professional advice to address this gum disease before it progresses to a more severe form of gum disease known as periodontitis.
When gingivitis is not treated, periodontitis may cause the affected area to weaken the tooth. Periodontitis diseases are mainly the results of infections and inflammation of the gum and bone that support the teeth. Mostly seen in adults, the gums may pull away from the tooth, the bone loss, causing nearby teeth to loosen.
As the disease progresses, your mouth will become more vulnerable to infections due to the open plaque “deposits”. Therefore, it is important to acknowledge the early signs and symptoms and receive treatment in the early stages of illness to avoid surgical procedures post-diagnosis.

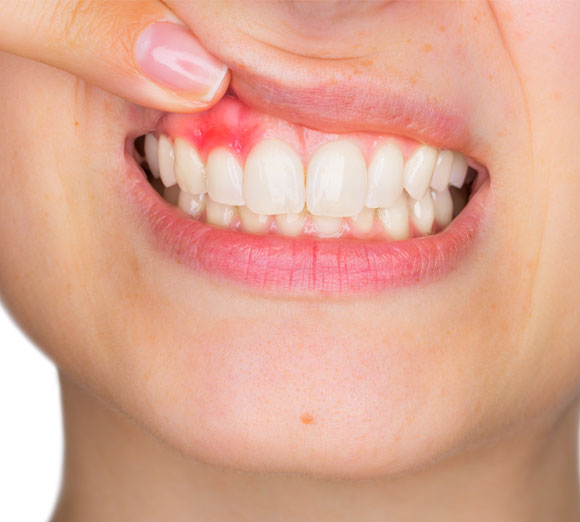
Signs and Symptoms
- Bad breath
- Tender or bleeding gums
- Irritable, red and swollen gums
- Loose and sensitive teeth
- Gums that have pulled away from your teeth
- Pus between the gums and teeth
Prevention and Treatment
Gingivitis can be treated with good oral hygiene and regular professional cleaning. It is recommended you brush twice daily and to also floss daily to remove the soft plaque deposits, as well as having a professional clean once every six months to remove any hardened plaque.
More severe forms of periodontal disease can also be treated including deep cleaning of the tooth root surfaces below the gums, taking soft tissue grafts -taking tissue from your palate and placing this where your gum is in recession, and prescription -using antibiotics to help treat the disease.

